
Robotic arm assisted Total Knee Replacement
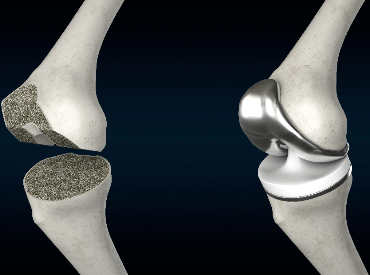
What is it?
Total knee replacement (TKR) is performed to treat arthritis that is established and extensive.
Normally, the joint surfaces are covered by a smooth, frictionless surface called articular cartilage. When this wears away, the joint surfaces become rough causing pain, swelling, deformity, restriction of movement and function and stiffness.
This procedure replaces the worn surfaces of the joint with artificial surfaces, and in doing so, relieves pain, swelling and stiffness, improves range of movement and function and corrects alignment.
It is a very successful treatment for the majority of patients and Dr Shiva is one of the very few orthopaedic surgeons in India who is trained and approved to use the MAKO stryker system for robotic joint replacement.
Who should have a Total Knee Replacement?
The decision to undergo any form of replacement surgery should be based around your quality of life; surgery is usually considered the last resort option, particularly when other treatment is not adequate or is no longer beneficial, thus leading to deterioration in quality of life.
Non-operative treatments include but are not limited to, physiotherapy, analgesia, cortisone injections, joint supplements and weight loss.
Will I need any tests/scans?
X-rays will be requested for all cases. With the advent of robotic assisted surgery, CT scans will also be required pre-operatively.
How is it done?
The surgery is usually carried out under spinal or general anaesthetic. A tourniquet is applied and inflated. The incision is made at the front of your knee, in the midline. The worn areas of the joint are removed and the implant is fixed into place, usually using special bone cement. The implant is essentially made up of two metal alloy parts and a polyethylene (high grade plastic) insert. The movement and stability of the joint are checked. The wound is closed with sutures and clips. A dressing and bandage are then applied.
If robotic-arm assistance is utilised (Stryker-MAKO), a robotic arm removes the worn areas of the joint.
The procedure normally takes between 1-2 hours.
How long is the hospital stay?
Your stay in hospital will approximately be between 5-10 days. Safely regaining mobility with crutches and being able to go up and down stairs are pre-requisites for discharge. Post-operatively, a blood test and an X-ray will be taken.
What about after I leave hospital?
You will see a physiotherapist before discharge to be instructed on crutch use and simple exercises to carry out in the short term. Crutches are advised for approximately 4-6 weeks, but this varies from patient to patient.
You will be allowed to weight-bear as tolerated in most cases. Swelling of the knee and lower leg and bruising is very common after total knee replacement and is to be expected. It may persist for several weeks until full range of motion and mobility has been regained.
You will be prescribed analgesia to take home You will also be prescribed anti-coagulant medication to take for a further 14 days or until you are fully mobile. This is to minimise the risk of a deep vein thrombosis.
You will see Dr Shiva two weeks after surgery for a wound check (and stitch/clip removal) and a physiotherapy program will ensue thereafter which is paramount to the success of the operation. Dr Shiva will liaise with him/her in detail to advise on the post-operative exercise program.
Total recovery time is between 4-6 months. Gradual improvement is seen during this period and Dr Shiva advises driving can resume once he has seen you and consented.
It is good and common practice to keep uni-compartmental and total knee replacements under regular review to ensure they are performing adequately. Thus routine follow up should be organised. Dr Shiva would like to see you for clinical examination and X-ray your knee at the following post-operative intervals:
• 6 weeks (no X-ray required)
• 6 months
• 1 year
• 2 year
• 5 years
• 10 years
• Every 5 years after that
What are the potential complications?
All surgery carries a risk. Specific risks to total knee replacement are:
Infection – this can be either superficial (wound) or within the joint. Antibiotics will be given to reduce this risk.
Thrombosis – a clot in the deep veins of the lower limb (DVT). The risk is minimised by early mobility and anti-coagulant medication. Oral contraceptive pills and HRT, which are known to increase risk, should be stopped before surgery.
Bleeding – this may require a return to the operating room for removal of blood clots and to stop the bleeding.
Stiffness – It is very important that some mobility of the knee is maintained after surgery. The physiotherapist will advise on simple exercises that can be carried out at home. Dr Shiva also recommends that you take regular analgesia and use ice to help minimise post- operative discomfort and facilitate early movements.
Loosening – the implant can become loose, either due to infection or as a function of time. It will need to be replaced in either case.
Residual symptoms – unfortunately, no guarantees can be offered regarding curing your symptoms, despite the surgeon’s best efforts. In this case, further management and treatment options will be discussed with you.
