
Procedures
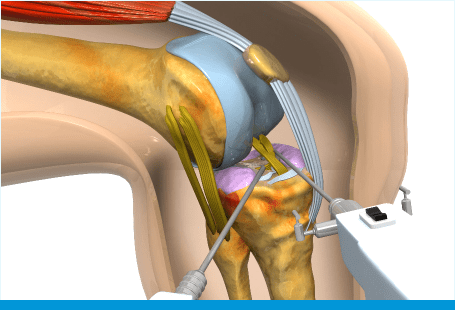
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
It is a procedure that aims to reconstruct the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), commonly after the native ACL has been ruptured. It is performed arthroscopically, using either the patients’ own tendon tissue (autograft) or donated tendon tissue (allograft).
Multi-ligament Injury
Multi-ligament injuries of the knee are serious injuries where more than one of the following structures are damaged (ruptured, partially ruptured/torn, strained) at the same time


Multi-ligament Injury
Multi-ligament injuries of the knee are serious injuries where more than one of the following structures are damaged (ruptured, partially ruptured/torn, strained) at the same time
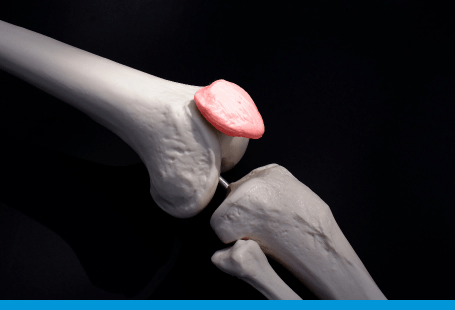
Patello-femoral Instability
This is a complex condition where the patella (kneecap) repeatedly slips out of position fully (dislocation) or partially (subluxation). This normally happens towards the outside of the knee (laterally).
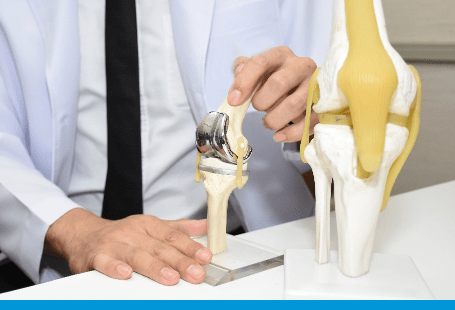

Patello-femoral joint replacement is performed for arthritis that solely affects the patello-femoral joint (kneecap joint). The patello-femoral joint is made up of the patella (kneecap) and the end of the thighbone (femur) that articulates with the patella the trochlea.
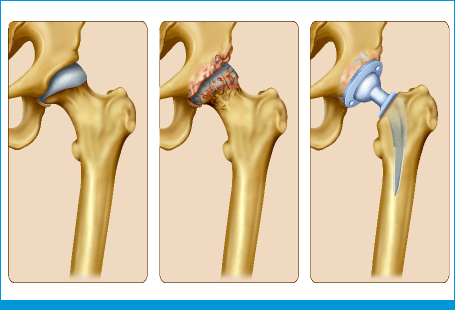
The hip joint is a ball (femoral head) and socket (acetabulum) joint. The joint surfaces are lined with smooth cartilage (articular). A special layer called the capsule or synovium lines the joint. The socket has a fibro- cartilaginous ring surrounding it called the labrum, which acts as a fluid seal and enhances joint stability.
Uni-compartmental or uni-condylar knee replacement is where only one part of the knee is replaced. It used to treat arthritis (wearing away of the smooth articular cartilage).
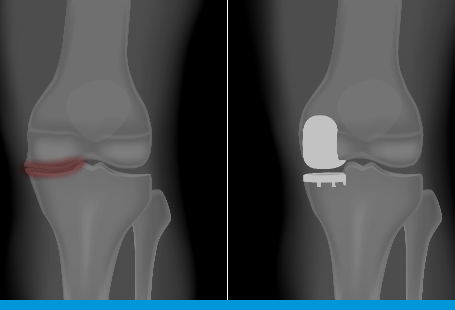

Uni-compartmental or uni-condylar knee replacement is where only one part of the knee is replaced. It used to treat arthritis (wearing away of the smooth articular cartilage).
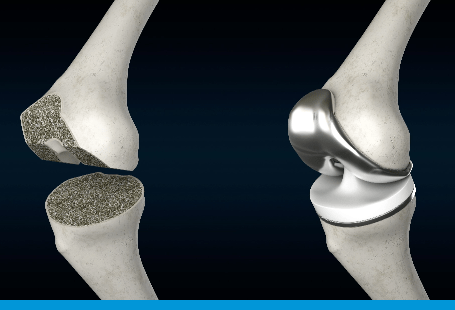
Total knee replacement (TKR) is performed to treat arthritis that is established and extensive. Normally, the joint surfaces are covered by a smooth, frictionlemgss surface called articular cartilage. When this wears away, the joint surfaces become rough causing pain, swelling, deformity, restriction of movement and function and stiffness.
Knee arthroscopy is a keyhole procedure of the knee that can be used as a diagnostic tool or to treat a variety of pathology/conditions within the knee accurately.
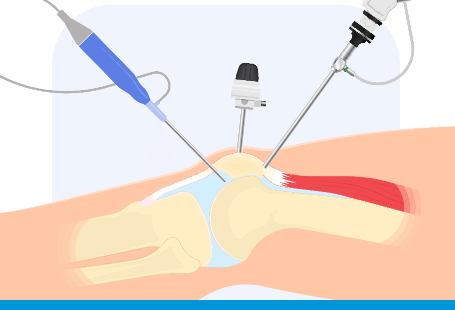

Knee Arthroscopy
Knee arthroscopy is a keyhole procedure of the knee that can be used as a diagnostic tool or to treat a variety of pathology/conditions within the knee accurately.
